Overview
Our challenge focuses on developing methods for lung nodule detection and lung nodule classification from Chest X-Ray images.
- Lung nodule detection is performed through a lung classification task into two categories, lung containing nodules and healthy lungs.
- Lung nodule localization which consists of finding the center point of nodules in chest x-ray images.
The competition is open to any teams from universities, research institutes, or industry labs of which at least one member holds a Ph.D in computer science, biomedical engineering, or radiology.
Dataset
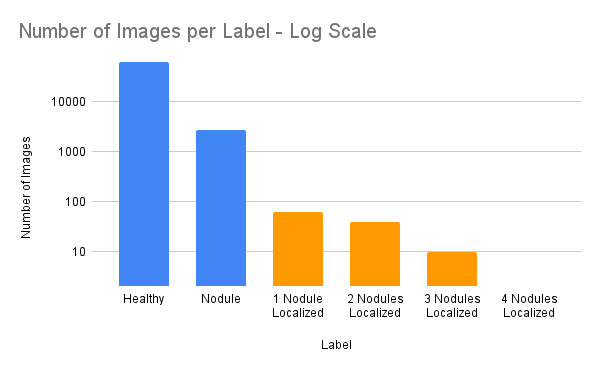
The competitors will be provided with a single original dataset including 66110 images of frontal radiographs as JPG images and associated ground truths, namely class label (presence, absence of nodules), and pixel coordinates corresponding to positions of nodules for a subset of images labeled nodule positive. This set has been generated by filtering existing datasets. The participants can train their models on additional datasets upon request and organizer authorization. If this rule is not respected, the team’s work will not be considered for the competition. The dataset for this challenge comes from two sources, introducing natural variability in acquisition protocols and patient populations. The dataset also contains relatively few annotated images for the second task, reflecting real-world challenges in handling class imbalance and heterogeneous data. By framing the challenge around these constraints, we aim to highlight scientifically relevant issues and encourage the development of algorithms that are robust, generalizable, and clinically meaningful. The test set that will be used in the experimental study comes from a different data source which differs from the training dataset. The training dataset will be available for downloading once the team’s registration is complete.
Evaluation
Classification metrics: For the classification task, standard metrics will be used, including accuracy, recall, precision, F1. Localization metrics: For the localization task, a custom metric based on weighted distances will be used.
Submission
Final submissions will need to provide
- The complete source code shared via a public github repository for testing reproducibility of the results. This code will need to stay publicly available afterwards.
- A summary of the approach including the following points:
- Definition of loss functions and evaluation metrics used for the two tasks
- The training time
- The inference time
- Hardware used for the training of the approaches
- Size of the model in terms of parameters
Teams are authorized to submit only one method for each task.
Tentative Schedule Timeline & Registration
- January 12, 2026: Dataset is made available, and participants are allowed to run their calculations.
- February 13, 2026: Registration deadline. Registration must be sent to Adnan Mustafic, Karim Hammoudi, Halim Benhabiles and Adnane Cabani before February 13th, 2026. Register here
- March 13, 2026: Submission deadline of the results to the organizers.
- March 29, 2026: Communication of the results to the participants.
- April 13, 2026: Submission of the report to ArXiV including the top 10 approaches.
- April 20, 2026: Submission of the report into a Q1 elsevier journal article. Discussions with editors are in progress.
Registration
Registration must be sent to Adnan Mustafic, Karim Hammoudi, Halim Benhabiles and Adnane Cabani before February 13th, 2026. Register here The email must contain the following information:
- Your teamname for the challenge
- The list of participants and their affiliations
References
B. Slika, F. Dornaika and K. Hammoudi, « Multi-Score Prediction for Lung Infection Severity in Chest X-Ray Images » in IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 2052-2058, 2025, doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3359082.
B. Slika, F. Dornaika, F. Bougourzi and K. Hammoudi, « PViTGAtt-IP: Severity Quantification of Lung Infections in Chest X-Rays and CT Scans via Parallel and Cross-Attended Encoders » in IEEE Transactions on Big Data, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 2736-2748, 2025, doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2025.3556612.
B. Slika, F. Dornaika, F. Bougourzi and K. Hammoudi, « Transformer-Based Lung Infection Severity Prediction with Cross Attention and Conditional TransMix Augmentation » in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR) Workshops, Multimodal Learning and Applications (MULA), pp. 212-221, 2025. https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2025W/MULA2025/papers/Slika_Transformer-Based_Lung_Infection_Severity_Prediction_with_Cross_Attention_and_Conditional_CVPRW_2025_paper.pdf
Z. Yang, H. Benhabiles, F. Windal, J. Follet, AC. Leniere, D. Collard, « A Coarse-to-Fine Segmentation Methodology Based on Deep Networks for Automated Analysis of Cryptosporidium Parasite from Fluorescence Microscopic Images » in Medical Optical Imaging and Virtual Microscopy Image Analysis. MOVI 2022. Held in conjunction with MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13578. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-16961-8_16.
K. Hammoudi, H. Benhabiles, M. Melkemi, F. Dornaika, I. Arganda-Carreras, D. Collard, A. Scherpereel, « Deep Learning on Chest X-ray Images to Detect and Evaluate Pneumonia Cases at the Era of COVID-19 ». Journal of Medical Systems 45, 75, 2021, doi: 10.1007/s10916-021-01745-4.
Affiliation
This challenge is an initiative of the GT-I2MDP (Working Group on Image and Multimodal AI for Pulmonary Pathology Diagnosis) part of the GdR IASIS (Information, Learning, Signal, Image, and Vision).
For more information about our activities, please visit:
- The GT-I2MDP website: https://gt-i2mdp.github.io/website/
- The GdR IASIS website: GdR IASIS Website